Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yagafarov, O.; Katayama, Yoshinori; Brazhkin, V. V.*; Lyapin, A. G.*; Saito, Hiroyuki
High Pressure Research, 33(1), p.191 - 195, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
Ikeda, Takashi
no journal, ,
Molecular vibrational spectroscopies via infrared (IR) absorption or Raman scattering are widely employed to explore possible phases of materials under study irrespective of their thermodynamic states. Tominaga  successfully performed the IR and Raman experiments for ambient and supercritical water. They found that a peak corresponding to the bending mode observed around 1600 cm
successfully performed the IR and Raman experiments for ambient and supercritical water. They found that a peak corresponding to the bending mode observed around 1600 cm for ambient water vanishes from the Raman spectrum of supercritical water, while the corresponding peak remains clearly visible in the measured IR spectrum. This observation cannot be explained unless dynamical and electronic properties of water under pressure are considered explicitly. Thus, in this contribution, a theoretical formulation is developed for computing the IR and Raman spectra via first principles molecular dynamics. Then we demonstrate that the above-mentioned experimental findings for water are well reproduced in our computational scheme.
for ambient water vanishes from the Raman spectrum of supercritical water, while the corresponding peak remains clearly visible in the measured IR spectrum. This observation cannot be explained unless dynamical and electronic properties of water under pressure are considered explicitly. Thus, in this contribution, a theoretical formulation is developed for computing the IR and Raman spectra via first principles molecular dynamics. Then we demonstrate that the above-mentioned experimental findings for water are well reproduced in our computational scheme.
 at high pressures and high temperatures for development of novel Ti-based hydrides
at high pressures and high temperatures for development of novel Ti-based hydridesEndo, Naruki; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
Watanuki, Tetsu; Kawana, Daichi*; Machida, Akihiko; Tsai, A. P.*; Kashimoto, Shiro*; Tanaka, Yukinori*; Ishimasa, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Teruo*; Sato, Taku*
no journal, ,
Quasiperiodic intermediate-valence systems were prepared by applying pressure to Yb-based quasicrystals. In these systems, each quasiperiodic lattice point has a charge degree of freedom. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments near the Yb L3-edge demonstrate that the Yb valence in a Cd-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal increases continuously upon compression from a divalent state at ambient pressure and reaches 2.33 at 31.7 GPa, where the quasiperiodically arranged Yb ions take a valence fluctuation state. For the case of a Cd-Mg-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal, the Yb valence reaches a value of 2.71 at 57.6 GPa. By following the trend of Yb-based intermediate-valence crystalline compounds, this large valence increase suggests that the 4f electron system in this quasicrystal varies from a valence fluctuation regime to a strong correlated electron regime. Additionally, we have recently found that Au-Al-Yb icosahedral quasicrystal is an IV compound at ambient pressure.
Machida, Akihiko; Hattori, Takanori; Honda, Mitsunori*; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated the structural properties of rare-earth metal hydrides under high pressure. LaH has the CaF
has the CaF type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH
type structure in which the H atoms locate at the tetrahedral interstitial sites (T-sites) of the fcc metal lattice. Synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and infrared reflection experiments revealed disproportionation reaction of LaH into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH
into the H-poor and H-rich phases around 11 GPa. Before the disproportionation reaction, we have found that the fcc metal lattice transformed into tetragonal lattice. The ordering of the H atoms in the octahedral-sites (O-sites) causes the tetragonal distortion of LaH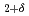 . The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH
. The tetragonal transformation and successive disproportionation reaction of LaH would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD
would closely relate to the inter-site transfer of the H atoms between the T- and O-sites. We have performed the neutron diffraction experiments of LaD to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
to investigate the change of the positions and occupancies of the hydrogen atoms under high pressure.
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Utsumi, Wataru; Yagi, Takehiko*
no journal, ,
Beamline "PLANET" at BL11, MLF in J-PARC is aimed at investigating hydrogen in minerals and rocks in the earth's interior. To generate high pressure and high temperature conditions, 6-rams multi-anvil press "ATSUHIME" is installed in BL11. The press consists from six hydraulic rams mounted on a flame with maximum load of 500-ton in each ram. Three types of experimental mode are available: (1) hydrostatic experiment, (2) uni-axial experiment and (3) deformation experiment. Typical sample size is 4 mm phi and 4 mm h when Truncated Edge Length (TEL) of 10 mm 6-6 anvil is used. Generated pressure was determined by resistance measurement experiment of Bi. Bi III-V transition at 7.7 GPa was detected at 1390 kN /1 ram for TEL10, 644 kN /1 ram for TEL 7 6-6 anvil. The detail of design and performance of the 6-rams press will be presented.
Osakabe, Toyotaka
no journal, ,
Recently, We have developed indispensable high-pressure techniques for single-crystal magnetic neutron diffraction experiments beyond 3 GPa. One is a hybrid-anvil device which has an opposed pair of a supported SiC anvil by MP35N alloy and a WC anvil with a small hollow on the culet. In a feasibility test, we could generate pressures of 10 GPa at a load of 3.8 tons with high stability. Another is a pressure-transmitting medium with low compressibility and good hydrostaticity under high-pressure. We found that glycerin meets the requirements at least up to 7 GPa. We also developed a thermal neutron focusing device with a lot of curved supermirrors for high-pressure experiments with tiny samples. Using the high-pressure techniques described above, we have so far intensively performed high-pressure single-crystal magnetic neutron diffraction experiments at JRR-3. As an example, we will present the results of the experiments on filled skutterudite PrFe P
P up to 10.5 GPa.
up to 10.5 GPa.
 C
C under high pressure; A Single-crystal neutron diffraction study
under high pressure; A Single-crystal neutron diffraction studyYamauchi, Hiroki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Matsuoka, Eiichi*; Onodera, Hideya*
no journal, ,
Fukazawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
I report recent neutron diffraction studies of ferroelectric ices and hydrates under high pressure, which carried out at neutron facilities (J-PARC at Tokai, HFIR and SNS at Oak Ridge). Time-resolved diffraction experiments at Oak Ridge show that ferroelectric ice and hydrates with hydrogen-ordered arrangement nucleates and grows with time. High-resolution powder diffraction studies at J-PARC show the existence of the ferroelectric ice under high-pressure and its formation from compressed amorphous ice. The results suggest that a cool icy body in space has a thick layer of ferroelectric ice. Furthermore, I report spectral and vibrational properties of ferroelectric ices investigated by inelastic neutron scattering and infrared absorption measurements.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Nagai, Takaya*; Utsumi, Wataru; Iitaka, Toshiaki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Inoue, Toru*; Yagi, Takehiko*
no journal, ,
The PLANET is the new high-pressure neutron beamline constructed at the intense pulsed neutron source J-PARC. This beamline aims at revealing the effect of water on dynamics of the interior of the Earth and planets by using the neutron character that is sensitive to hydrogen. The most characteristic feature of this beamline is to possess the huge 6-axis press with the maximum load of 500 ton/axis, which can simultaneously generate high-pressure and high-temperature condition of 20 GPa and 2000 K (see Sano-Furukawa et al.). Coupled with the state-of-the-art techniques of neutron diffraction and radiography, the beamline offers the microscopic and macroscopic information of materials at high-PT condition. In the last Spring, we finished the beam commissioning. I introduce the general feature of this beamline and the specification revealed by the commissioning. The beamline is used by the project members before the next March, and then it will be opened for general users.
Sekine, Yurina; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Arakawa, Masashi*; Abe, Jun; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Utsumi, Wataru; Arima, Hiroshi*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya; Komatsu, Kazuki*; et al.
no journal, ,